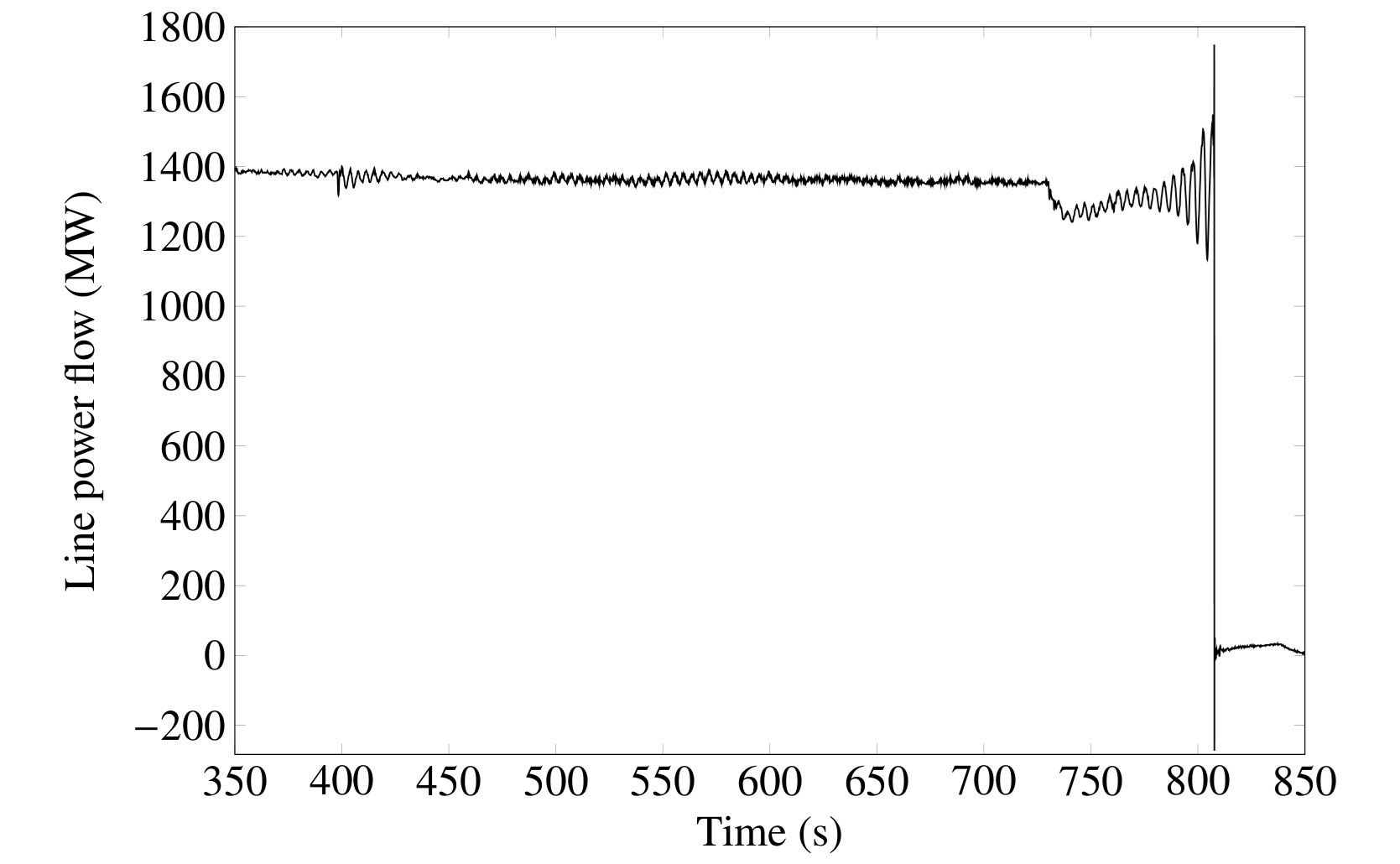
Power System Oscillations
Chapter 1: Introduction
Abstract
Electric power systems are among the largest structural achievements of man. Some transcend international boundaries, but others supply the local needs of a ship or an airplane. The generators within an interconnected power system usually produce alternating current, and are synchronized to operate at the same frequency. In a synchronized system, the power is naturally shared between generators in the ratio of the rating of the generators, but this can be modified by the operator. Systems, which operate at different frequencies, can also be interconnected, either through a frequency converter or through a direct current tie. A direct current tie is also used between systems that, while operating at the same nominal frequency, have difficulty in remaining in synchronism if interconnected.