Power System Oscillations
Chapter 12: Measurement-Based Modal Analysis
Abstract
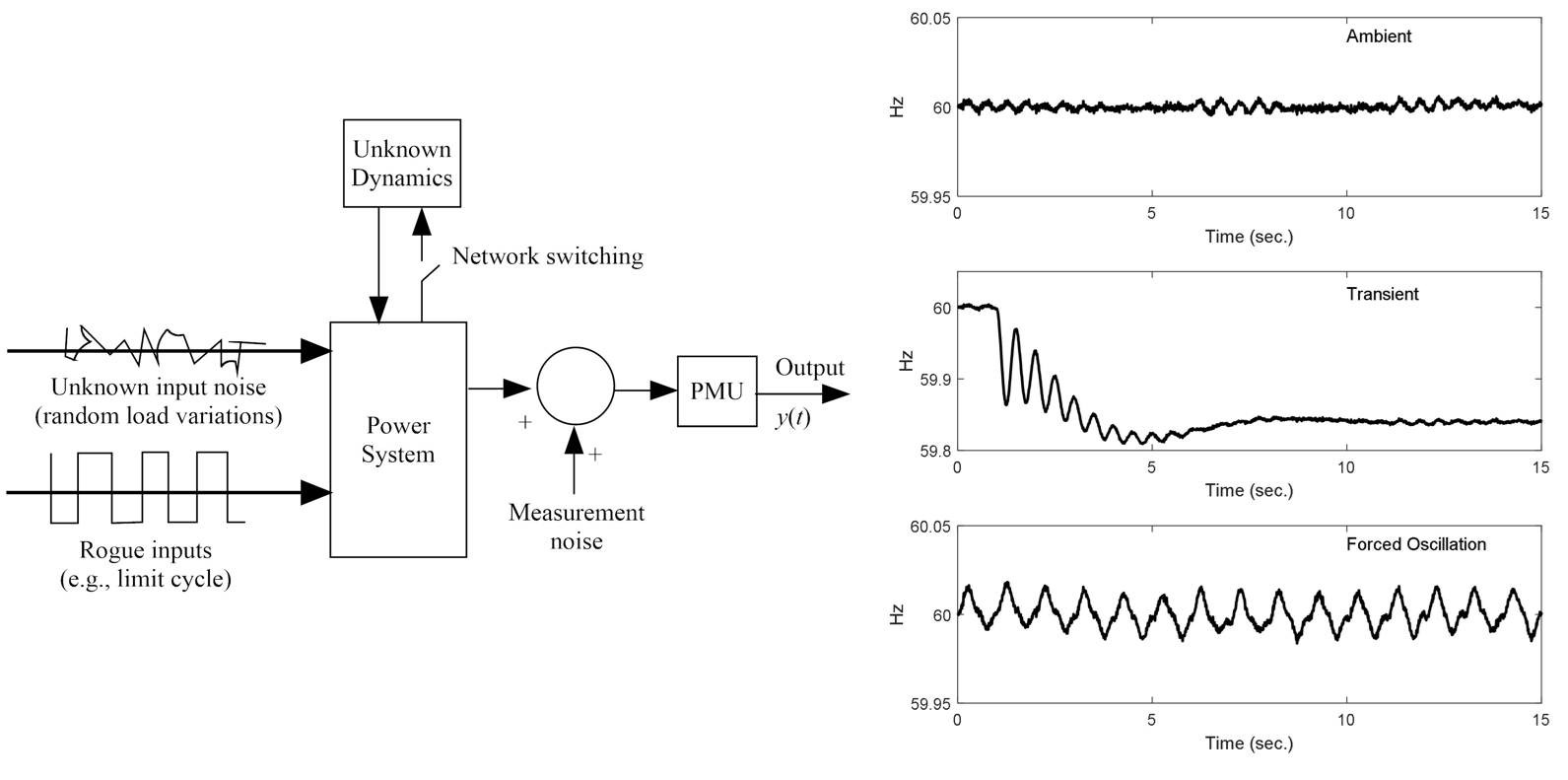
Chapter 3 establishes the use of modal analysis to characterize small-signal dynamic properties that are necessary for comprehending a system’s stability traits and for designing stabilizing control systems. The foundation of the modal analysis is that small system motions can be described by a linear ordinary differential equation (ODE). In Chapter 3, the ODE parameters are obtained by linearizing a nonlinear dynamic model. In this chapter, we explore methods for obtaining a system’s modal characteristics directly from actual-system time-synchronized phasor measurements. We term this measurement-based modal analysis. The obvious advantage of the measurement-based approach is that it does not require a system differential equation model. One directly analyzes actual-system measurements to obtain the modal characteristics.